一种基于 LOUDS 编码的压缩字典树
最近在学习 ElasticSearch 的 FST 索引结构发现,它的底层实现结构依然有对象头和指针的开销,如果能把这部分开销去掉,压缩率还能再上一层楼。于是经过调研发现一类叫“简洁数据结构”的结构,实现了占用极小且查询高效。遂深入探索,于是就有了这篇文章。
p.s. 部分参考图和代码源自《基于 LOUDS 的 Succinct Set 详解》
简介
什么是 Succinct 数据结构?
简洁数据结构(Succinct Data Structures)是指一类在存储数据时接近信息熵下界,同时保持高效查询性能的数据结构,也就是说一个结构表示的所占空间接近信息熵下限,那么就可以称其为“简洁的”。其核心原理就是使用 Bitmap 来表示数据结构以节省大量空间。
Succinct 思想常被应用于对列表和树的存储以压缩空间,也就是 “Succinct Vector” 和 “Succinct Tree”
一些常见的简洁数据结构实现包括:
- 小波树:在压缩的序列上支持丰富的序列查询操作,如第k小查询,区间统计
- FM-Index:在一个压缩后的文本索引中,极快地查找一个模式串 P 出现的所有位置(全文索引)
- 简洁树:用极小的空间存储树结构,并支持高效的基础导航操作
- 简洁图:基于邻接表的简洁表示,以极小空间占用支持图的各种基本操作
- 简洁向量:就是简洁数组,比一般的基本数据类型数组还要小
原理
Succinct Trie = Succinct Tree + Trie Label
因为我探索的主要是如何让 FST 更省空间,FST 本质上也是个 Trie 树,就打算从 Trie 出发,结合上文简介中说到的 “Succinct Tree”,探索能否将 Trie 树和 Succinct Tree 结合在一起。当然,最终结果当然是可以的,已经有很多篇文章实现了。因此接下来我将从核心原理开始讲起,一步步去实现一个占用极小空间又能高效查询的 Succinct Trie
编码
结合简洁数据结构的核心思想,我们不难推测:Succinct Trie 核心原理是使用 Bitmap 来表示 Trie 树结构,因此我们先要将树结构编码成 bit 序列
目前有两种主流编码方式,DFOUS 支持更多的功能,LOUDS 有更快的性能:
- LOUDS:按 BFS 遍历树,对于每个节点,用一元编码(一串 1 加一个 0)表示它的度数。适用于度数大、深度浅的树,如 Trie 树
- DFUDS:按 DFS 遍历树,对每个有 d 个子节点的节点,用一个 “(” 和 d 个 “)” 来表示,但整个序列用额外的 “(“ 开头以保证平衡。可以理解为特殊的括号序列,编码时 “(” 为 1,“)” 为 0。适用于要深度优先遍历的场景,如语法分析树、DOM 树
因为我们的目标在 Trie 树上,所以我们这里主要探讨 LOUDS 编码方式
什么是 LOUDS 编码?
Level-Order Unary Degree Sequence,层序一元度序列,简称 LOUDS。听起来高大上,实际内容非常简单
以下图这一颗 Trie 树为例,对于每个节点,用 0 表示子节点,1 表示结束。比如,节点 1 有两个子节点,那么就表示成 001。 最终按照 BFS 顺序把所有编码排列一起就是这棵树的 LOUDS 编码
综上,该树的 LOUDS 编码为 001 001 01 01 01 01 01 1 1 1
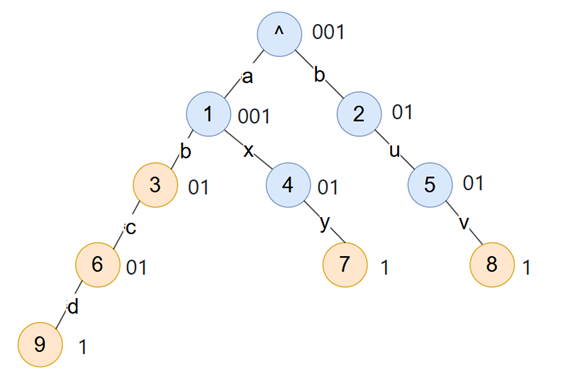
注 1:节点标签,即图中节点间边上的那些字符,本身并不属于树结构的一部分,所以需要另外使用一个数组 labels 存储
注 2:原论文中的标准形式应该是用 1 表示子节点,0 表示结束
导航
现在我们把一个 Trie 树压成一串 bit 序列装进位图里,那么我们现在如何从这一坨序列中还原出 Trie 树呢?或者说我们如何在这一坨被压缩的 Trie 树中进行导航操作?
这时候就需要额外定义四个辅助方法来操作:
rank1(pos):返回位图 [0, pos] 下标范围内 1 的个数;rank0 则是 0 的个数
select1(k):返回位图里第 k 个 1 的下标位置;select0 则是 0 的位置
实际进行导航中会频繁调用这几个方法,因此为了提高性能,我们会预计算这些方法的值
我们用上文图一的 Trie 树来展示如何通过这四个方法来在树节点之间随意转移
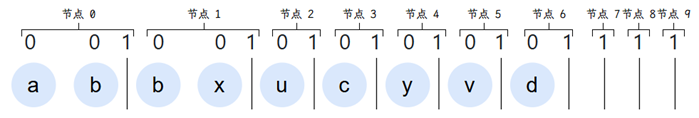
上图是该 Trie 树经过 LOUDS 编码出的 bit 序列与其源节点的对应关系,可以帮助理解
以节点 1 为例,它的子节点是 3、4,父节点是 0,那么:
- 节点 1 起始 bit 位置 =
select1(1)+1=3 - 节点 1 第一子节点编号 =
rank0(3 + 0)=3 - 节点 1 第二子节点编号 =
rank0(3 + 1)=4 - 节点 1 的父节点起始 bit 位置 =
select0(1)=0,父节点编号 =rank1(select0(1))=rank1(0)=0 - 如果知道当前节点编码和当前 bit 位置,那么当前节点标签 =
labels[index - nodeId]
以上操作说明如何从节点 1 向上(回溯)和向下(递归)两个方向的导航,并且展示了当获取到当前节点编码和当前 bit 位置,如何获取当前节点标签。既然上下节点都能遍历,那遍历整棵树自然不在话下
实现
我们在上文已经简单讲解了 Succinct Trie 的压缩方式(编码)和遍历方法(导航),说白了就是通过一种精心设计过的编码方式将树型结构的节点信息存储到 bit 序列中,然后通过四个辅助方法提取这些信息直接计算出原始信息,理解后其实也没那么难
下面是用 Java 简单实现的一个基于 LOUDS 编码的静态压缩 Trie 树,按照简洁数据结构的分类,可以被称为 Succinct Trie。该实现无第三方依赖,创建后不可更改结构,理论上支持各种前缀树特性,目前只实现一些主要功能:
boolean contains(String key):判断 key 是否存在int index(String key):若 key 存在,则会返回内部对应的节点 ID;否则,返回 -1String get(int nodeId):通过给定节点 ID 反向搜索 keyIterator<String> iterator(boolean orderly):以字典序或层序的顺序遍历 Trie 中所有的 keyIterator<String> prefixKeysOf(String str):查询给定字符串在 Trie 内所有的前缀Iterator<String> prefixSearch(String prefix):查询所有以给定前缀开头的 key
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.util.*;
public class SuccinctTrie {
private final char[] labels; // 存储 Trie 树的字符标签
private final BitVector labelBitmap; // 存储 LOUDS 编码的位向量
private final BitVector isLeaf; // 存储所有叶子节点标记的位向量
public static SuccinctTrie of(String... keys) {
return new SuccinctTrie(keys);
}
private SuccinctTrie(String[] keys) {
for (int i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
assert keys[i].compareTo(keys[i - 1]) >= 0 : "The inputs are not ordered!";
}
List<Character> labelsList = new ArrayList<>();
BitVector.Builder labelBitmapBuilder = new BitVector.Builder();
BitVector.Builder isLeafBuilder = new BitVector.Builder();
Queue<Range> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(new Range(0, keys.length, 0));
int bitPos = 0, nodeId = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Range range = queue.poll();
int L = range.L, R = range.R, index = range.index;
isLeafBuilder.set(nodeId, keys[L].length() == index);
// 处理子节点
int start = L;
while (start < R) {
// 跳过长度不足的键
if (keys[start].length() <= index) {
start++;
continue;
}
char currentChar = keys[start].charAt(index);
int end = start + 1;
while (end < R) {
if (keys[end].length() <= index || keys[end].charAt(index) != currentChar) {
break;
}
end++;
}
// 添加子节点标签
labelsList.add(currentChar);
// 设置子节点标记(0)
// labelBitmapBuilder.set(bitPos, false);
bitPos++;
// 将子节点范围加入队列
queue.add(new Range(start, end, index + 1));
start = end;
}
// 设置节点结束标记(1)
labelBitmapBuilder.set(bitPos++, true);
nodeId++;
}
// 转换并初始化位图
this.labels = new char[labelsList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < labelsList.size(); i++) {
labels[i] = labelsList.get(i);
}
this.labelBitmap = labelBitmapBuilder.build(true);
this.isLeaf = isLeafBuilder.build(false);
}
/**
* 存储的 key 的个数
*/
public int size() {
return isLeaf.oneCount;
}
/**
* 该 Trie 树的节点个数
*/
public int nodeCount() {
return isLeaf.size;
}
/**
* 判断 key 是否存在
*
* @param key 要查询的键值
* @return 是否存在
*/
public boolean contains(String key) {
return index(key) >= 0;
}
/**
* 精确查询给定 key 在内部唯一对应的节点 ID
*
* @param key 要查询的 key
* @return 如果 key 存在,则返回对应的节点 ID;否则,返回 -1
*/
public int index(String key) {
int nodeId = extract(key);
return nodeId >= 0 && isLeaf.get(nodeId) ? nodeId : -1;
}
/**
* 反向查询给定节点 ID 在内部唯一对应的 key
*
* @param nodeId 要查询的节点 ID
* @return 如果节点 ID 在合法范围内,则返回对应的 key;否则,返回 null
*/
public String get(int nodeId) {
if (isLeaf.get(nodeId)) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
int bitmapIndex;
while ((bitmapIndex = labelBitmap.select0(nodeId)) >= 0) {
nodeId = labelBitmap.rank1(bitmapIndex);
str.append(labels[bitmapIndex - nodeId]);
}
return str.reverse().toString();
}
return null;
}
/**
* <p>以字典序或层序的方式遍历 Trie 中所有的 key</p>
* <b>注意</b>:层序遍历的性能要优于字典序遍历,如果不追求有序,请将 {@code orderly} 设为 false 以获得最佳性能
*
* @param orderly 如果为 true,则按(DFS)字典序遍历;如果为 false,则按层序遍历。
* @return 一个用于遍历所有 key 的迭代器
*/
public Iterator<String> iterator(boolean orderly) {
if (orderly) {
return traverse(0, "");
} else {
return new Iterator<>() {
private int index = isLeaf.nextSetBit(0);
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index >= 0;
}
@Override
public String next() {
String str = get(index);
index = isLeaf.nextSetBit(index + 1);
return str;
}
};
}
}
/**
* 查询给定字符串在 Trie 内所有的前缀
*
* @param str 要查询的字符串
* @return 一个用于遍历所有前缀的迭代器
*/
public Iterator<String> prefixKeysOf(String str) {
return new TermIterator() {
private final char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
private int pos = 0;
private int nodeId = 0;
private int bitmapIndex = 0;
{
advance(); // 初始化查找第一个前缀
}
@Override
protected void advance() {
while (pos < chars.length) {
int index = labelSearch(nodeId, bitmapIndex, chars[pos]);
if (index < 0) {
break;
}
nodeId = index + 1 - nodeId;
bitmapIndex = labelBitmap.select1(nodeId) + 1;
pos++;
if (isLeaf.get(nodeId)) {
next = new String(chars, 0, pos);
return;
}
}
next = null;
}
};
}
/**
* 查询所有以给定前缀开头的 key
*
* @param prefix 要搜索的前缀
* @return 一个用于遍历所有匹配前缀的 key 的迭代器
*/
public Iterator<String> prefixSearch(String prefix) {
return traverse(extract(prefix), prefix);
}
private int extract(String key) {
int nodeId = 0, bitmapIndex = 0;
for (char c : key.toCharArray()) {
if ((bitmapIndex = labelSearch(nodeId, bitmapIndex, c)) < 0) {
return -1;
}
// 向子节点转移
nodeId = bitmapIndex + 1 - nodeId;
bitmapIndex = labelBitmap.select1(nodeId) + 1;
}
return nodeId;
}
private Iterator<String> traverse(int rootId, String prefix) {
return new TermIterator() {
private final CharBuffer charBuffer = CharBuffer.allocate(256);
private int nodeId = rootId;
private int bitmapIndex = rootId < 0 ? labelBitmap.size : labelBitmap.select1(rootId) + 1;
{
charBuffer.append(prefix);
charBuffer.flip();
if (!isLeaf.get(rootId)) {
advance();
}
}
@Override
protected void advance() {
// 切换写模式
charBuffer.position(charBuffer.limit());
charBuffer.limit(charBuffer.capacity());
while (true) {
// 撞墙
while (bitmapIndex >= labelBitmap.size || labelBitmap.get(bitmapIndex)) {
// 到达根节点,遍历结束
if (nodeId == rootId) {
next = null;
return;
}
// 回溯并向右转移
bitmapIndex = labelBitmap.select0(nodeId) + 1;
nodeId = bitmapIndex - nodeId;
charBuffer.position(charBuffer.position() - 1);
}
charBuffer.put(labels[bitmapIndex - nodeId]);
// 向下转移
nodeId = bitmapIndex + 1 - nodeId;
bitmapIndex = labelBitmap.select1(nodeId) + 1;
if (isLeaf.get(nodeId)) {
charBuffer.flip();
next = charBuffer.toString();
return;
}
}
}
};
}
/**
* 搜索标签向下层转移
*
* @param nodeId 当前节点ID
* @param bitmapIndex 当前节点在 {@code labelBitmap} 中的起始下标
* @param b 要搜索的标签
* @return 目标标签在 {@code labelBitmap} 中的下标,否则返回 -1
*/
private int labelSearch(int nodeId, int bitmapIndex, char b) {
while (true) {
if (bitmapIndex >= labelBitmap.size || labelBitmap.get(bitmapIndex)) {
return -1;
}
int labelIndex = bitmapIndex - nodeId;
if (labelIndex < labels.length && labels[labelIndex] == b) {
break;
}
bitmapIndex++;
}
return bitmapIndex;
}
// 辅助类:表示键范围
private record Range(int L, int R, int index) {
}
// 词项迭代器
private abstract static class TermIterator implements Iterator<String> {
String next = "";
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
@Override
public String next() {
if (next == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
String term = next;
advance();
return term;
}
abstract void advance();
}
// 自实现位向量(位图)
public static class BitVector {
/**
* 数值越小,selects 预计算的间距越小,占用更高,select1 的性能越好
* 经测试,设为 1 或 2 时,性能提升明显,但占用极高,其余数值影响不大
*/
private static final int GAP = 64;
private final long[] bits;
private final int[] ranks; // 预计算rank1
private final int[] selects; // 部分预计算select1
public final int oneCount;
public final int size;
// 构建器模式
public static class Builder {
private final List<Long> bits = new ArrayList<>();
private int size = 0;
private int count = 0;
public void set(int position, boolean value) {
ensureCapacity(position);
int block = position >> 6;
int offset = position & 0x3F;
long mask = 1L << offset;
long oldBlock = bits.get(block);
if (value) {
bits.set(block, oldBlock | mask); // 设置位为1
} else {
bits.set(block, oldBlock & ~mask); // 设置位为0
}
// 仅当位的值实际发生变化时更新计数器
if ((oldBlock & mask) == 0 == value) {
count += value ? 1 : 0;
}
}
private void ensureCapacity(int position) {
int requiredBlocks = (position >> 6) + 1;
while (bits.size() < requiredBlocks) {
bits.add(0L);
}
size = Math.max(size, position + 1);
}
public BitVector build(boolean rankSelect) {
long[] array = new long[bits.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < bits.size(); i++) {
array[i] = bits.get(i);
}
return new BitVector(array, size, count, rankSelect);
}
}
private BitVector(long[] bits, int size, int count, boolean rankSelect) {
this.bits = bits;
this.size = size;
this.oneCount = count;
// 预计算rank和select
if (rankSelect) {
int totalOnes = 0;
int oneCount = 0;
this.ranks = new int[bits.length + 1];
List<Integer> selectList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < bits.length; i++) {
ranks[i] = totalOnes;
int blockOnes = Long.bitCount(bits[i]);
totalOnes += blockOnes;
long block = bits[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 64; j++) {
if ((block & (1L << j)) != 0) {
oneCount++;
if (oneCount % GAP == 0) {
selectList.add(i * 64 + j);
}
}
}
}
ranks[bits.length] = totalOnes;
this.selects = new int[selectList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < selectList.size(); i++) {
selects[i] = selectList.get(i);
}
} else {
this.ranks = null;
this.selects = null;
}
}
public int nextSetBit(int from) {
if (from < 0 || from >= size) {
return -1;
}
int u = from >> 6;
long word;
for (word = this.bits[u] & -1L << from; word == 0L; word = this.bits[u]) {
if (++u == bits.length) {
return -1;
}
}
return (u << 6) + Long.numberOfTrailingZeros(word);
}
public boolean get(int pos) {
if (pos >= size) return false;
int block = pos >> 6;
int offset = pos & 0x3F;
return (bits[block] & (1L << offset)) != 0;
}
public int rank1(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= size) {
return 0;
}
int block = pos + 1 >> 6;
int offset = pos + 1 & 0x3F;
int count = ranks[block];
if (offset > 0) {
long mask = (1L << offset) - 1;
count += Long.bitCount(bits[block] & mask);
}
return count;
}
// 性能较差
public int select1(int k) {
if (k <= 0 || k > ranks[bits.length]) {
return -1;
}
// 使用预计算的select加速
if (k % GAP == 0) {
int idx = k / GAP - 1;
if (idx < selects.length)
return selects[idx];
}
// 二分查找块
int low = 0, high = ranks.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + high >>> 1;
if (ranks[mid] < k) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid;
}
}
int block = low - 1;
// 在块内查找
int remaining = k - ranks[block];
long word = bits[block];
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
if ((word & (1L << i)) != 0) {
if (--remaining == 0) {
return block * 64 + i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public int rank0(int pos) {
if (pos >= size) {
pos = size - 1;
}
return pos + 1 - rank1(pos);
}
// 性能极差
public int select0(int k) {
if (k <= 0 || k > ranks[bits.length]) {
return -1;
}
int low = 0, high = size - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
// 计算[0, mid]区间内的0的个数
if (rank0(mid) < k) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
// 满足rank0(low) >= k的最小位置即第k个0的位置
return low;
}
}
}
没有全面的测试,简单测试大致结果如下,测试很粗糙,仅供参考:
- 中文 key:内存占用比 FSA 小 40% 左右,查询性能比 FSA 要低 76%
- 英文 key:内存占用比 FSA 大 8.8% 左右,查询性能比 FSA 要低 64%(英文字符在 char 类型也是用 2 字节存,比较吃亏)
因为是最简实现,没有进行任何优化,但确实能看出在内存方面有一定优势,后续引入第三方库(Sux4J)优化,表现肯定会强上不少,有很大的发展潜力
注:FSA 是没有输出 FST,即不存 Value 的 FST,因为 Succinct Trie 只能存 Key,相当于 Set 集合,直接跟存储键值对的 FST 对比不合适